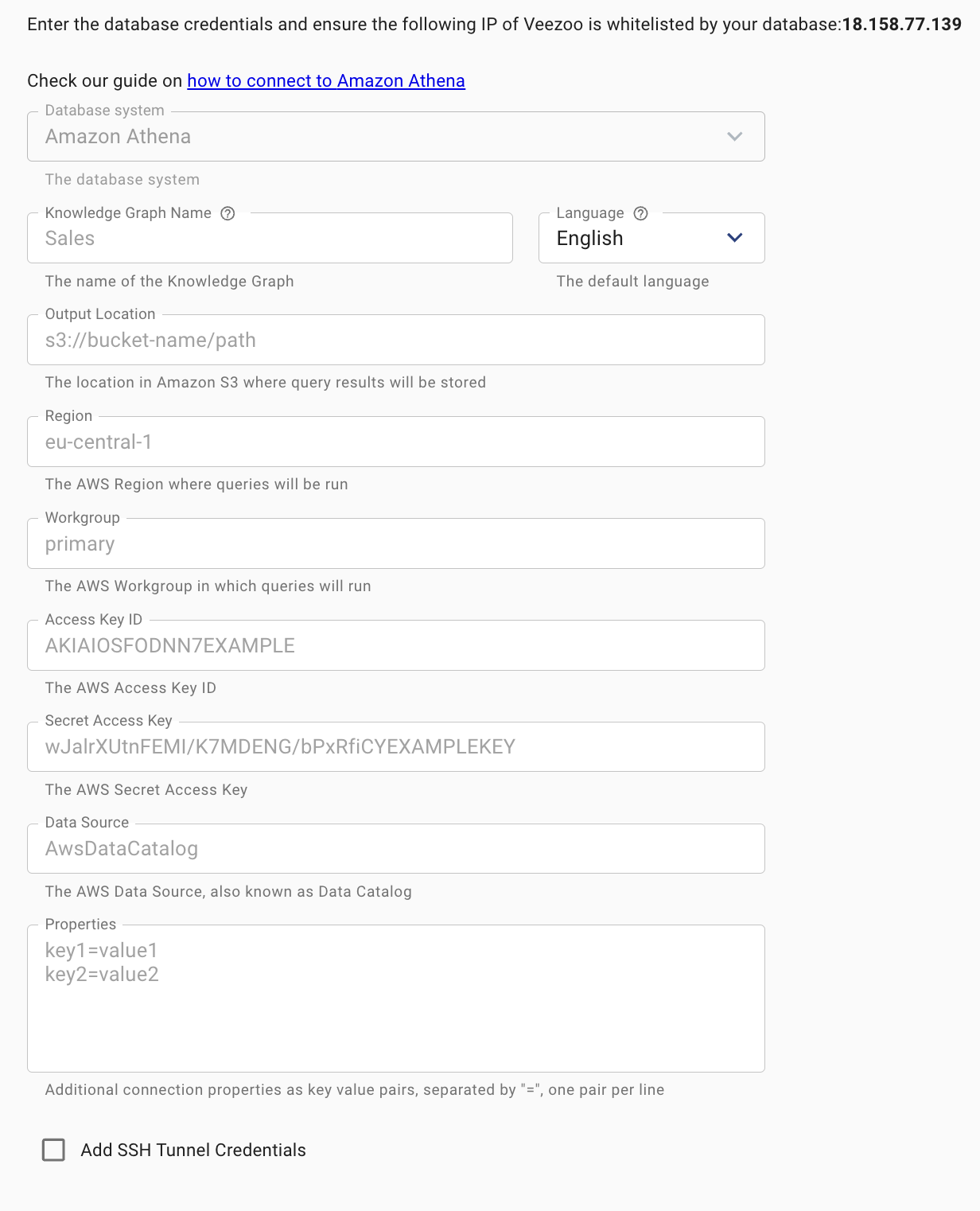
Connecting to Amazon Athena
The following guide shows how to configure Veezoo to connect to Amazon Athena.
Creating IAM Credentials
Veezoo communicates with Amazon Athena with IAM credentials: an access key ID and a secret access key.
We recommend creating a new IAM user specifically for Veezoo, with the minimum required permissions.
We recommend to use the permissions described below on the new IAM user. Adjust the resource names in the policy as needed for your environment, for example s3 bucket names, workgroup, glue catalog, database names and tables. In this example we use eu-central-1 as our region, 123456789 as our account number, athena_workgroup as our workgroup, and athena_db as our database. We give access to all tables in this database: "arn:aws:glue:eu-central-1:123456789:table/athena_db/*"
More details about a connection failure might appear in the Athena Recent Queries section, accessible from the Amazon Athena query editor.
First, the following permissions gives your IAM user acess to required Athena and Glue resources:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowAthenaMetadata",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"athena:GetTableMetadata",
"athena:ListEngineVersions",
"athena:ListDataCatalogs",
"athena:ListDatabases",
"athena:GetDatabase",
"athena:ListTableMetadata",
"athena:ListWorkGroups"
],
"Resource": "*"
},
{
"Sid": "AllowAthenaDB",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"athena:CreatePreparedStatement",
"athena:StartQueryExecution",
"athena:GetQueryResultsStream",
"athena:UpdatePreparedStatement",
"athena:GetQueryResults",
"athena:DeletePreparedStatement",
"athena:DeleteNamedQuery",
"athena:GetNamedQuery",
"athena:GetPreparedStatement",
"athena:ListQueryExecutions",
"athena:ListNamedQueries",
"athena:GetWorkGroup",
"athena:CreateNamedQuery",
"athena:StopQueryExecution",
"athena:GetQueryExecution",
"athena:BatchGetNamedQuery",
"athena:ListPreparedStatements",
"athena:BatchGetQueryExecution"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:athena:eu-central-1:123456789:workgroup/athena_workgroup",
]
},
{
"Sid": "AllowGlue",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"glue:GetTables",
"glue:GetDatabases",
"glue:GetTable",
"glue:GetDatabase"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:glue:eu-central-1::catalog",
"arn:aws:glue:eu-central-1:123456789:database/athena_db",
"arn:aws:glue:eu-central-1:123456789:table/athena_db/*"
]
}
]
}
Second, the IAM user will also need access to the S3 buckets where the data lives and where the query output will be stored. This example uses athena-query-output-bucket as our output bucket and the data bucket that our athena tables use is athena-data-bucket. Adjust these as needed.
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Sid": "AllowQueryOutput",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:Get*",
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::athena-query-output-bucket",
"arn:aws:s3:::athena-query-output-bucket/*"
]
},
{
"Sid": "AllowAccessToData",
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:Get*",
"s3:List*"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:s3:::athena-data-bucket",
"arn:aws:s3:::athena-data-bucket/*"
]
}
]
}
Note that the S3 Bucket URL needs to appear both with and without the root path (with a wildcard), in the Resource section.
See this guide to learn more about creating access keys for an IAM user.
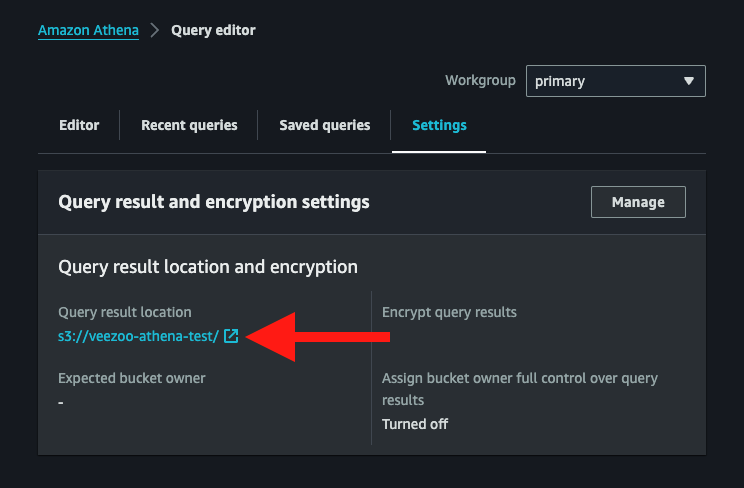
Finding the Query Output Location
Amazon Athena stores query results in a S3 Bucket. Create a new Bucket on the Amazon S3 console, or choose an existing one if it is appropriate. The query output location field also accepts Bucket URLs without a path, to save the result files in its root.
A query output location could have been set earlier in the settings of the Amazon Athena Query Editor. If so, using a different location for Veezoo only is also possible.
Read more about query output locations here.
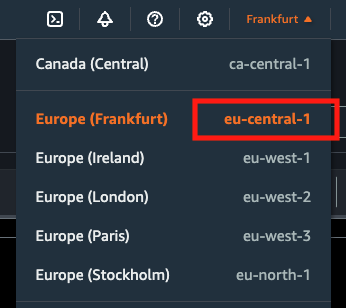
Finding the Region
The current AWS region is displayed in the top right corner of the Amazon Athena console.
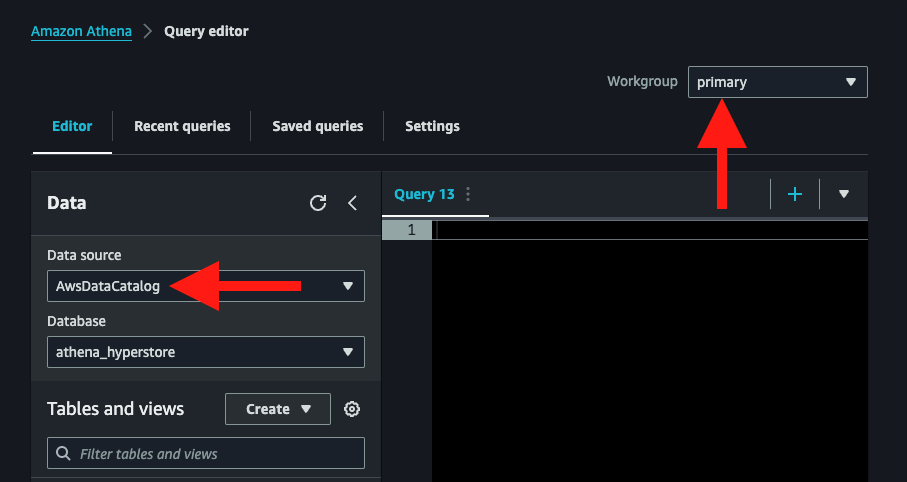
Finding the Workgroup and Data Source
From the Amazon Athena Query Editor, select the Workgroup and Data Source (also called Data Catalog) you want to connect to.